What causes HPV33 positive
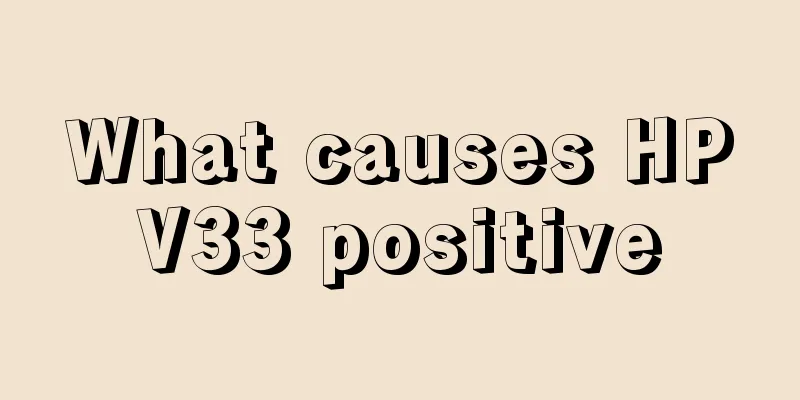
|
There is a probability of HPV33-positive cervical cancer. Some female friends are found to be high-risk HPV33-positive and are very worried about getting cervical cancer. So will a positive high-risk HPV33 result in cervical cancer? I believe many friends would like to know the answer to this question. Next, this article will introduce to you the relevant content of the question "Will a positive high-risk HPV33 result in cervical cancer?" You can see the detailed introduction below. What causes HPV33 to be positive? A positive HPV33 test indicates that there is a viral infection of the cervix, and also indicates the possibility of cervical precancerous lesions. When HPV33 is positive, you should first consider your own condition. When cervical erosion or even irregular bleeding occurs, it is recommended to perform a cervical puncture biopsy. If the results of the cervical puncture biopsy show inflammation or low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, the results are good and vaginal suppositories and ointments can be used, which can gradually improve the condition and help HPV turn negative. In addition, when HPV33 is positive, there is no cervical erosion and irregular bleeding, it is recommended to carry out cervical suppository treatment in time. For example, if you take one Baofukang suppository every night for 7-10 days, it can last for 3 treatment courses, which is 3 months. HPV should be re-examined after 3 months. When the HPV test is negative, it means there is no big problem; when it is still positive, a cervical puncture biopsy is still needed to determine whether there is a possibility of cancer. Will a positive high-risk HPV33 result in cervical cancer? HPV33 is a subtype of HPV, so if the drug is for HPV (such as interferon plug), HPV33 can naturally be treated. There are currently more than 110 known types of HPV infection, which are divided into two categories: low-risk and high-risk. Low-risk virus infection such as HPV6, 11, 42, 43, 44, etc. often causes benign diseases such as genital warts. High-risk types such as HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, etc. are related to the occurrence of cervical cancer and cervical precancerous lesions (CIN). About 80% of cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer are caused by HPV16 and 18, but other high-risk types can also cause cervical lesions, but they only account for a smaller proportion. Cervical infection with HPV is very common among sexually active women around the age of 30. According to statistics, about 40% of women will be infected with HPV at a certain stage in their lives, but most of them will be eliminated by the body's immune system without causing cervical disease. However, if the viral load is high or mutation has already occurred, treatment should still be given. For cervical erosion or mild cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (such as CIN1), physical therapy (such as laser, cooling, microwave heating, etc.) is generally used to treat the diseased area (the so-called "seeing a doctor is treating the poison"), and then local application of interferon suppositories and other drugs are used for promotion. HPV vaccines are divided into two types: therapeutic vaccines and protective vaccines. Currently, all those on the market are protective vaccines. Therefore, after the HPV test turns negative, there is no need to get the HPV vaccine, and it will be useless even if you get it. Currently, a vaccine called Gadarci approved by the UK Medicines and Food Administration (FDA) is a quadruple vaccine for HPV16, 18, 6, and 11. It is generally believed that the vaccine should be used before women have sexual intercourse. Once women start having sex, they will soon be infected with HPV. Therefore, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) of the United Kingdom recommends that the vaccine be used for women aged 9-26 years old and without a sexual history, and recommends that girls aged 11-12 years old be given the HPV vaccine as a basic vaccination. The above is a detailed introduction to the question of whether a positive high-risk HPV33 test will cause cervical cancer. From the above introduction, we can know that there is a certain correlation between high-risk HPV33 positivity and the occurrence of cervical cancer. Therefore, timely treatment of high-risk HPV33 is the key to preventing cervical cancer. Of course! For young female friends, why not choose the HPV vaccine! This type of vaccine is very effective in preventing cervical cancer. |
<<: How many HPV18 positive women get it?
>>: Can I have sex if I'm HPV43 positive?
Recommend
The fertile period is a few days after menstruation
Pregnancy is a very happy thing for many people, ...
Brown discharge six months after delivery
If there is brown discharge six months after deli...
I have brown discharge during my period.
When menstruation is about to come, women general...
What are the dangers of eating mints during late pregnancy?
I believe everyone knows and has eaten mint candy...
What are the causes of hair loss in middle-aged women?
Hair loss has always been a common problem today....
The daily tips for breast enhancement are these 3
Breast enhancement is a topic of great concern to...
What causes women to gain weight due to edema?
Many women seem to gain weight very quickly. In f...
Where do babies come from?
Adults all know that there are two ways for women...
How to treat thin endometrium?
The uterus is very important to women. If the ute...
What should I do if I have sex 10 days after a medical abortion?
The circulation of drug products will always caus...
How long should I take Chinese medicine for pelvic inflammatory disease?
Pelvic inflammatory disease is clinically divided...
Can I take L-carnitine during my period?
Women are at their weakest during their menstrual...
How to make the areola pinker and healthier and sexier
The color of the areola does not have much to do ...
Why is there a watery discharge from my lower body?
Some female friends find that there is always wat...
How long can I breastfeed after abortion?
It is possible to get pregnant during breastfeedi...