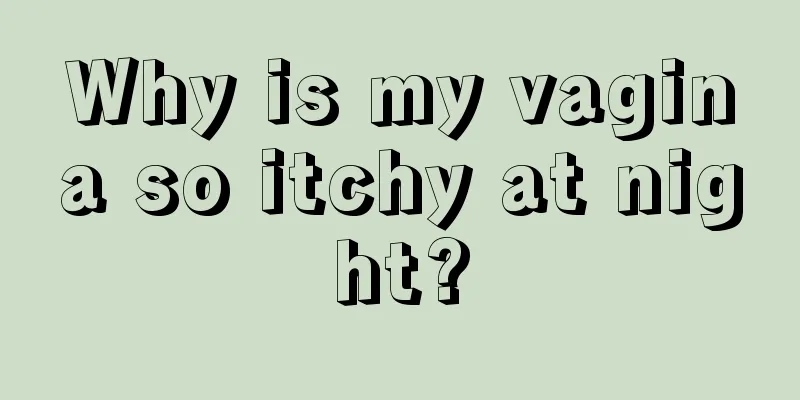Female reproductive organs diagram

|
Female genitals, including female internal genitalia and female reproductive organs. The female reproductive organ refers to the exposed part of the male reproductive organ, also known as the private parts. Including the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular function, Bartholin's glands, vestibular bulbs, urethral orifice, vulva and ruptured hymen. The female internal reproductive system consists of the location of the prostate (uterus and ovaries), the reproductive ducts (bilateral fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina). The uterus is the place where the fetus is created. The sperm and egg combine to form an embryo here, which gradually develops into a complete fetus. After full term, the uterus contracts and the fetus is delivered. The ovaries are women's sex hormone organs, which contain many eggs, which can produce and release oocytes, secrete estrogen, and maintain women's unique endocrine system and secondary sexual characteristics. After menopause, the uterus and ovaries gradually shrink. Female genitalia Yindi The clitoris is a hard structure, homologous to the male genitalia, located just below and behind the labia majora. There are two corpora cavernosa inside the clitoris. The corpus cavernosum of the clitoris penis can be divided into three parts: the clitoral crus, the clitoral body and the clitoral glans. The clitoral crus is cylindrical, adhered to the sciatic nerve branch and the inferior phalangeal branch, and covered with the sciatic cavernous muscle. Around the lower part of the ischial tuberosity, the two clitoral crus connect to form the clitoral body. There is an indetailed corpus cavernosum septum (also known as the pectinate septum) between the two clitoral bodies to separate them. The clitoral body folds forward and downward, and its mineral end is the glans clitoridis. The glans clitoridis is a small ring-shaped nodule with a diameter of 6 to 8 mm and is surrounded by the clitoral hood. Smegma often appears in the clitoral groove between the glans clitoridis and the clitoral hood. The lower part of the clitoral glans is connected to the labia minora by the frenulum. The outer part of the clitoral cavernous body is covered with a folded membrane, and the outer part of the tunica albuginea is covered with the clitoral muscle fascia. There are two connective tissue cords, one superficial and one deep, between the clitoral body and the ischial tuberosity. The superficial cord is the clitoral cruciate ligament, and the deep cord is called the clitoral suspensory cruciate ligament. The corpus cavernosum of the clitoris can also swell and become hard. The peripheral nerves of the glans clitoris are rich and colorful, with high sensitivity, which can easily cause hardness due to excessive tension. It is an important structure for sexual sensation. Vulva refers to a woman's external sexual organ The mons pubis is the soft fleshy tissue under the male pubic hair that protects the female internal reproductive organs. The clitoral hood serves to protect the clitoris and is formed by the junction of the upper edges of the two labia minora. The labia majora are soft and rich in skin tissue, including glands that produce oil and a small amount of pubic hair. They are a pair of long, circular, raised skin folds on both sides of the private parts, close to the inner side of the thighs. It is connected to the mons pubis in front and the perineum in the back; it stretches downward and backward from the mons pubis, with the left and right labia majora united in front to form the anterior synapse, and the two ends at the back gathered to form the posterior synapse, which is located in front of the anus but is not as obvious as the anterior synapse. Male pubic hair grows outside the labia majora. The subcutaneous tissue is composed of human adipose tissue, collagen fibers and venous plexus, which can form abscesses after injury. Of course, the labia majora of single women are close together, covering the vulva and urethra. The labia majora of a primipara will separate to the sides due to the impact of childbirth. The labia minora are a pair of soft, mucous membrane wrinkles of skin located on the inner side of the labia majora, with a moist surface. The upper and lower branches of the labia minora cooperate with each other. The skin fold above is called the clitoral hood, and the skin fold below is called the clitoral frenulum, and the clitoris is located in the middle of them. The lower part of the labia minora gathers below the vulva, which is called the frenulum. There is a rich nerve distribution under the labia minora mucosa, so it feels sensitive. |
>>: Can the growth spots on adolescent girls be eliminated?
Recommend
Normal cervical picture HD
The cervix is one of the key organs in the fema...
How many days after cesarean section
A cesarean section is a surgery in which a doctor...
What causes vaginal bleeding in postmenopausal women?
Menopause in women refers to the decline of ovari...
When is it better for women to drink brown sugar water?
Women are more likely to use brown sugar water, w...
Dark brown blood on day 4 of period
Under normal circumstances, women have their peri...
Abdominal pain five days after miscarriage
Nowadays, medicine is becoming more and more deve...
How much weight gain is normal during pregnancy
Gaining weight during pregnancy is very normal. H...
What are the dangers of inner eyeliner?
Nowadays, many women who love beauty like to draw...
Why do I always feel cold during pregnancy?
Many mothers usually don't feel anything, but...
What causes swollen labia?
Whether male or female, the genitals are prone to...
What are the benefits of yoga for women
Good fitness methods will be welcomed by everyone...
Does taking Euthyrox during pregnancy have any effect on the fetus?
When a girl experiences her first pregnancy, her ...
What does it mean when a woman is wet down there?
I believe that most adults are quite curious. Dur...
How many days will you bleed after a miscarriage?
The first three months and the last three months ...
Does kidney deficiency affect fertility in women?
Kidney deficiency is a word that adults often com...