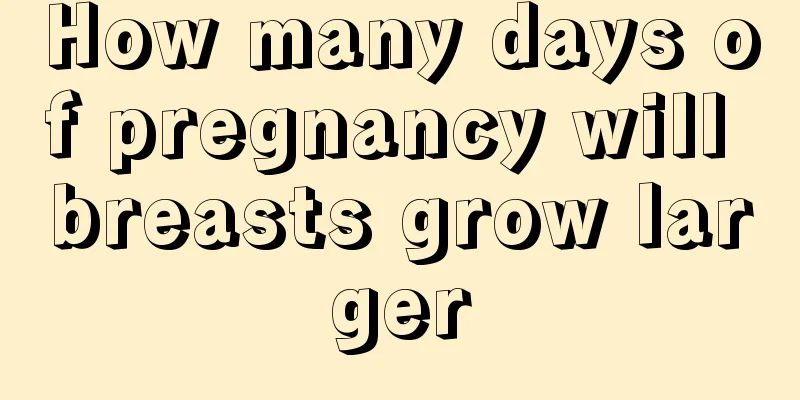Cervical polyp front cauliflower shape

|
Women will have some gynecological inflammation to a greater or lesser extent. Cervical erosion, vaginitis, etc. are all diseases that long-term plague women's health. Therefore, in daily life, you need to change your underwear frequently and wear loose and breathable bottoms. The cervix is where the vagina meets the entrance to the uterus. Inflammation here is very common. What is the reason why the front part of some people's cervical polyps appear cauliflower-shaped? How should we deal with it? What are polyps? Cervical polyps are caused by long-term chronic inflammation of the cervix, which stimulates the cervical mucosa and causes hyperplasia. The uterus has a natural ability to expel foreign matter, which causes the hyperplastic cervical mucosa to gradually protrude from the base to the external os of the cervix to form polyps. The polyp is red, tongue-shaped, soft and brittle, and easily bleeds when touched; cervical polyps also have a root, called a pedicle, which is generally slender and mostly attached to the external os of the cervix. Cervical polyps mostly grow individually and are shaped like soybeans. Some are as small as rice grains, while others are as large as 1 cm in diameter. Sometimes there may be several polyps. The incidence rate is about 5% among women of childbearing age and 4%-10% of all cervical lesions, and it is particularly common in women aged 30-49. Since the disease is related to inflammatory stimulation, sexual life and childbirth, married women account for more than 98% of the incidence. Cervical polyps are a common disease among women. If not treated early, it will not only endanger women's physical health, but also have a certain impact on their mental health. Therefore, female friends need to actively understand the symptoms of cervical polyps for early detection and prevention and maintenance. What are the obvious symptoms of cervical polyps? 1. Abnormal leucorrhea: Small cervical polyps are not easy to produce symptoms, and most patients are discovered during gynecological examinations. If the polyp is large, it will produce bloody leucorrhea or even contact bleeding, especially after sexual intercourse or straining to defecate, there will be a small amount of bleeding symptoms. Some patients usually have yellow leucorrhea, most of which have an odor or contain blood. 2. Abnormal vaginal bleeding: Cervical polyps lack obvious symptoms. Usually there is spotting of bright red blood, or a small amount of blood during sexual intercourse, which is mistakenly thought to be "menstruation". In a few patients, the amount of bleeding is similar to that of menstruation. Another symptom is vaginal bleeding after menopause, which is an obvious symptom of cervical polyps. At this time, the cause of bleeding should be found out as soon as possible. 3. Tumors flow out of the vagina: The most common symptom of cervical polyps is localized endometrial tumors protruding into the patient's uterine cavity. Sometimes they are single and sometimes they are multiple. They are gray-red, shiny, small in size, and have an average diameter of 0.5 to 2 cm. Small tumors are only 1 to 2 mm in diameter, while large and multiple tumors can fill the uterine cavity. The pedicles of patients with this disease vary in thickness and length, and the longer ones protrude outside the cervical opening. Those with shorter pedicles have diffuse growth. The surface of polyps often has symptoms of hemorrhagic necrosis, which can cause complications and infections. 4. Thrombosis in polyp vessels: If the pedicle is narrow, the blood flow should be reduced, the polyp is prone to degeneration, and thrombosis in the polyp blood vessels is likely to occur. Because of the blood stasis, it becomes an obvious symptom of cervical polyps, necrosis occurs at the top, and it may rot and fall off. Common causes of cervical polyps: 1. Inflammatory factors: It is generally believed that it is caused by long-term stimulation of chronic inflammation. Long-term inflammatory stimulation promotes excessive proliferation of cervical mucosa. In addition, the uterus has a tendency to expel foreign bodies, causing the hyperplastic mucosa to gradually protrude from the base to the external os of the cervix to form polyps. 2. Endocrine disorders: especially related to excessively high estrogen levels. Estrogen promotes the development of the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries themselves, and at the same time, the endometrium proliferates and produces menstruation. It can also promote the accumulation of subcutaneous fat, the retention of sodium and water in the body, and the deposition of calcium in the bones. 3. Pathogen infection: usually caused by delivery, miscarriage, postpartum infection, surgical operation or mechanical stimulation, sexual intercourse that damages the cervix, and pathogens invade and cause infection. What are the dangers of cervical polyps? 1. Female infertility: The formation and enlargement of cervical polyps will affect the shape of the cervical opening, which is not conducive to the passage of sperm, so there is a possibility of infertility. 2. Irregular bleeding: Patients with cervical polyps will experience abnormal bleeding and secretions during sexual intercourse. 3. Recurrent attacks: If only the polyps are removed, the chronic inflammation of the cervix is not eliminated and the pathogens are still lurking in the cervical tissue, so recurrence is still possible. Therefore, after treating cervical polyps, chronic cervical inflammation should also be treated to prevent recurrence of polyps. 4. Possibility of canceration: Polyp tissue has microvessels, and generally a cancer examination is required after resection. If malignant changes occur, further treatment is required. Most women who develop cervical polyps are middle-aged women. Now that you know what cervical polyps are, you should first prevent cervicitis when preventing them. Especially during menstruation, you must maintain good hygiene as it is very easy to be infected by bacteria. It is recommended to have a gynecological examination at least once a year. If any abnormality is found, early treatment can prevent the formation of polyps. |
<<: Medical abortion B-ultrasound showed clean bleeding without blood clots
>>: What are the symptoms of endocervical polypoid hyperplasia?
Recommend
What can I eat to increase my progesterone level if it is low?
Progesterone is a steroid that has a huge impact ...
Why is my period so little?
When a woman has her period every month, under no...
The pregnancy test stick showed two lines after half an hour.
Although pregnancy test sticks can detect whether...
What should I pay attention to after curettage?
Curettage is a common operation in clinical medic...
Can I eat honey during menstruation?
Menstruation refers to the menstrual period. Mens...
What are the effects of vasectomy on women?
For many families with children, contraceptive me...
Normal value of gestational sac at 12 weeks of pregnancy
The 12th week of pregnancy is a time of embryo de...
Is it necessary to observe confinement after miscarriage?
Young people are not responsible for their own bo...
What are the symptoms of early pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a very big thing for a woman, becaus...
What causes pain on the left side of the lower abdomen in women?
During menstruation, women often experience stoma...
What to wear during breastfeeding
Mothers who are breastfeeding do not have very st...
A woman dreamed of losing an upper tooth
If our success is to be multi-faceted, it is not ...
What are the traps for 30-year-old women to lose weight
After the age of 30, not only men are prone to ga...
Are there any pregnant women who have been bleeding during pregnancy?
Perhaps everyone knows that women will experience...
How to care after uterine myoma removal
Uterine fibroids are a very serious gynecological...