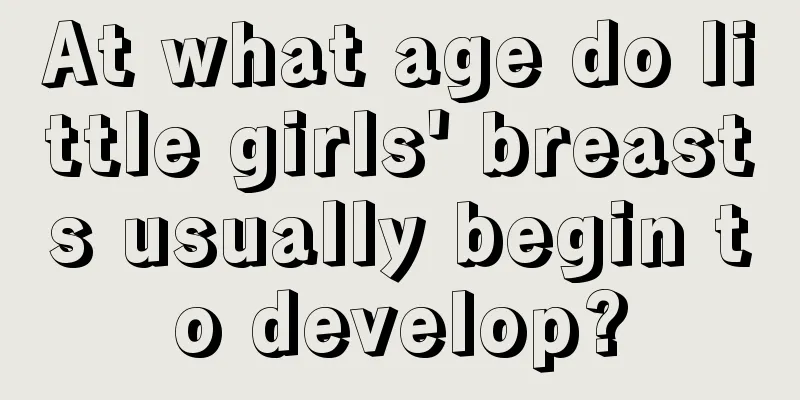Normal values of 6 female hormone tests

|
Female friends need to have a gynecological examination every six months. This is a very necessary examination. Any potential gynecological diseases can be detected through these examinations, especially the six hormone examinations, which are more critical. If these examination items are not in the normal value or are more serious, it means that the body has already had very serious lesions, and the next step of examination should be done based on the examination results. What are the normal values of the six estrogen test items? Estrogen is a steroid hormone that is mainly produced in the ovaries, follicles, corpus luteum and placenta during pregnancy. It has biological activity and the measurement of estrogen has certain value in gynecological diseases. The six normal values of estrogen are actually the six indicator ranges used to measure whether the amount of estrogen is normal, mainly including the following aspects: (1) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): promotes the development and maturation of ovarian follicles. Normal values: 1.5-10mIU/ml in the pre-ovulation period, 8-20mIU/ml in the ovulation period, and 2-10mIU/ml in the post-ovulation period. (2) Luteinizing hormone (LH): promotes ovulation, forms corpus luteum and secretes progesterone. Low FSH values are seen during estrogen-progestin treatment, etc. Normal values: 2-15mIU/ml in the preovulatory period, 30-100mIU/ml in the ovulatory period, and 4-10mIU/ml in the postovulatory period. (3) Prolactin (PRL): It is a simple protein hormone that promotes breast proliferation, milk production and milk discharge. Normal value: During the non-lactation period, the normal value of blood PRL is 0.08-0.92 nmol/L. A level higher than 1.0 nmol/L is considered hyperprolactinemia. (4) Estradiol (E2): Promotes the transition of the endometrium into the proliferative phase and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Normal value: The concentration of blood E2 is 48-521nmol/L in the preovulatory period, 70-1835nmol/L in the ovulatory period, and 272-793nmol/L in the postovulatory period, indicating premature ovarian failure and Sheehan's syndrome. (5) Progesterone (P): Promotes the transition of the endometrium from the proliferative phase to the secretory phase. Normal value: Blood P concentration is 0-4.8 nmol/L before ovulation and 7.6-97.6 nmol/L in the late ovulation period, which is seen in luteal insufficiency, ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding, etc. (6) Testosterone (T): About 25% is secreted by the adrenal cortex, and only 25% comes from the ovaries. Promote the development of the clitoris and mons pubis. Normal value: The normal concentration of T in female blood is 0.7-3.1 nmol/L. High blood T value can cause infertility. Six estrogen test precautions Women who experience menstrual cycle disorders, amenorrhea, abnormal genital bleeding, gynecological tumors, etc. need to undergo routine sex hormone tests for six items. For men, six items of sex hormones need to be checked when they have semen abnormalities, impotence, hormone-related tumors, etc. However, the content of sex hormone examination is the same for men and women. Sex hormone drugs (including progesterone and estrogen) should not be used at least one month before checking basic sex hormones, otherwise the results will be unreliable (except when sex hormones need to be rechecked after treatment). Sex hormones can be checked at any time during menstruation, as the normal values for each period are different. However, when diagnosing and treating infertility, it is necessary to understand the basic hormone level. First of all, the test should be done on the 2nd to 5th day of menstruation, which is called the basic hormone level. It is best to measure on the 3rd day. To confirm that it is the third day of menstruation, it is sufficient to check five sex hormones. Progesterone test is not necessary, as it should be tested during the luteal phase (21 days after menstruation or 7 days after ovulation). However, it is not certain whether vaginal bleeding is menstruation, and six items should be checked to prevent misdiagnosis. For patients with infrequent menstruation or amenorrhea, if the urine pregnancy test is negative, vaginal B-ultrasound examination shows no follicles ≥10mm in both ovaries, and EM thickness ﹤5mm, it can also be used as the basic status. The basic hormone test report should be read as follows: the normal values of basic LH and FSH are 5-10IU/L, the normal value of basic E2 is 25-50pg/ml (these 3 results cannot be compared with the reference values on the test report, but must be based on this standard); PRL and T can be compared with the reference values on the hospital's test report, and the normal value of P is shown below. |
<<: Ovulation day 8 pregnancy symptoms
>>: Know the boy or girl by looking at the endocrine system
Recommend
What to do if women have anal itching?
It is true that female friends are prone to some ...
When is the best time for a girl to get pregnant?
Although pregnancy is something that cannot be co...
50 days after delivery, I have some bleeding again. What's going on?
Under normal circumstances, there will be no blee...
Can I get pregnant if I have sex ten days before my period?
Normal women of childbearing age have a menstrual...
How to comfort a girl when she has a stomachache
Girls always have a few days a month, that is, th...
What to eat during menstruation?
Women are actually very weak during their menstru...
The woman squatted down and felt dizzy and black. What happened?
Many girls often encounter this problem, that is,...
How to choose autumn clothes for women
Autumn is a season that is neither too hot nor to...
Why does a woman's face turn yellow?
Nowadays, the pace of life in society is fast and...
How to solve the redness, swelling and pain in the genitals
Women naturally cannot avoid various gynecologica...
What causes women to have big eye bags?
Modern women are under great pressure in life. So...
How to use sanitary napkins for girls? This is the correct step!
Women will use sanitary napkins during their mens...
What are the symptoms of mid-stage breast cancer?
Breast cancer has become a major problem that soc...
What to do if something grows inside the vagina
A healthy woman actually needs to have healthy ge...
What are the signs of cervical cancer in women?
Cervical cancer is mainly a malignant disease tha...