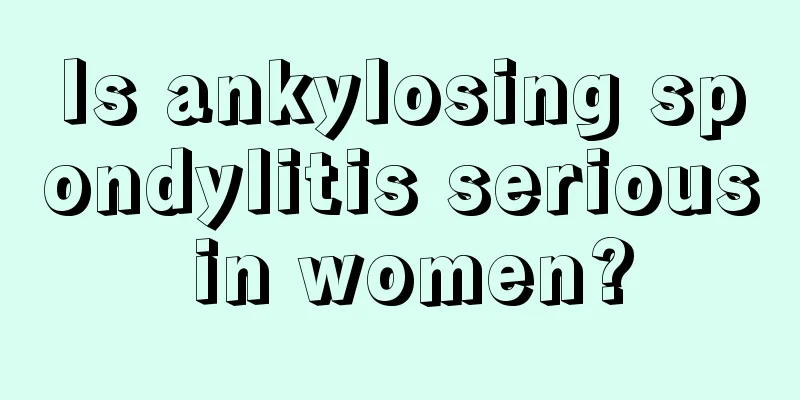Female genital anatomy

|
Compared with men, women have a more unique body structure and a more complex urinary system. Therefore, they are more prone to infection. So, what is the anatomy of the female genitals? Let's have a simple understanding and knowledge of this issue. I hope the following points will be of some help to everyone! Now let's take a look at the structure of the female reproductive organs. Female genitals, including female internal genitalia and female reproductive organs. The female reproductive organ refers to the exposed part of the male reproductive organ, also known as the private parts. Including the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular function, Bartholin's glands, vestibular bulbs, urethral orifice, vulva and ruptured hymen. The female internal reproductive system consists of the location of the prostate (uterus and ovaries), reproductive ducts (bilateral fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina). The uterus is the place where the fetus is created. The sperm and egg combine to form an embryo here, which gradually develops into a complete fetus. After full term, the uterus contracts and the fetus is delivered. The ovaries are women's sex hormone organs, which contain many eggs, which can produce and release oocytes, secrete estrogen, and maintain women's unique endocrine system and secondary sexual characteristics. After menopause, the uterus and ovaries gradually shrink. External male reproductive organs 1. Mons pubis. Located in front of the ischial tuberosity, it is a relatively protruding part. During puberty, pubic hair begins to grow on the skin. 2. Labia majora. There is a pair of raised skin wrinkles on both sides of the vulva, and they are double-sided. The outside is in contact with the skin, with rich sebaceous glands and sebaceous glands, and the inside is relatively moist, as if there is a mucous membrane. The labia majora of single women are of course closed, but due to the influence of childbirth, the labia majora of pregnant women will be separated to both sides. 3. Labia minora. Located on the inner side of the labia majora, it is a pair of thin wrinkled walls with moist surface, sebaceous glands, and rich nerve endings, so it is more sensitive. 4. Yindi. At the very front of the private parts, at the top between the labia minora on both sides, there are rich nerve endings and a large blood supply. It is very sensitive and will become hard when sexual pleasure is aroused. 5. Vaginal vestibule. In the diamond-shaped area between the labia minora, located between the labia minora on both sides and the clitoris. 6. Bartholin's glands. The size is similar to that of a cowpea, located behind the labia majora, covered with the bulbospongiosus muscle on the surface, and there is one on the top and bottom. Its effect is that when the couple's sexual intercourse is exciting, the secretion of the Bartholin's glands will increase, which can lubricate the vagina. 7. The hymen is broken. Located around the vulva, it is a layer of annular mucous membrane with a small gap in the middle, through which menstruation is discharged. It is 2mm thick and has a certain elasticity. It can be torn due to intense sports competition, labor, and straddle injuries. Internal male reproductive organs 1. In the vagina. It is the only way for couples to have sex and for pregnant women to give birth. It is the safe passage connecting the private parts and the uterus. It is located between the bladder, urethra and duodenum. 2. The uterus. It is shaped like an inverted pear, slightly flattened front and back, located in the center of the pelvis, and can be divided into two parts: the uterine body and the cervix. It is where newborns are created and menstruation occurs. 3. Bilateral fallopian tubes. A pair of long and curved tubes, about 12 cm long, are the safe channel for sperm and egg transportation, and an integral part of sperm and egg combination. 4. Uterus and ovaries. It is oval in shape and has reproductive and metabolic functions. It is the organ that produces oocytes and secretes hormones in women. |
<<: How to detoxify when you have acne caused by excessive internal heat
>>: How long does it take for the postpartum abdominal lumps to disappear?
Recommend
Bleeding after bed
Key reminder: In daily life, some women will expe...
What to do if one side of the breastfeeding mother has milk but the other side does not?
The breastfeeding period is a very important peri...
How to treat cervicitis
Many women will have such questions after being d...
Can I eat motherwort during menstruation?
In our country, it is very common for women to su...
What are the reasons for bleeding after sex?
Bleeding after sex is medically called intercours...
How long does it take for a woman to reach menopause?
Women will go through menopause when they reach a...
Is it normal for pregnant women not to gain weight?
Generally speaking, the weight of a pregnant woma...
What causes high testosterone in women?
High testosterone levels in women are caused by h...
What are the six female hormones?
There are a large number of different types of fe...
Why do nipples protrude?
The nipple is an indispensable part of the human ...
Is it serious if the lower edge covers the cervical opening?
The lower edge covering the cervical opening main...
How much does it cost to remove the IUD for women
Some pregnant women achieve the effect of sterili...
Traditional Chinese Medicine explains fetal arrest
Simply put, in the process of fetal growth, we ne...
How to remedy staying up late during menstruation
Under normal circumstances, women's menstruat...
Is the female bladder on the left or right?
The bladder is a very important organ for the hum...