Rabies Series 4 – What does the rabies virus do to the body?
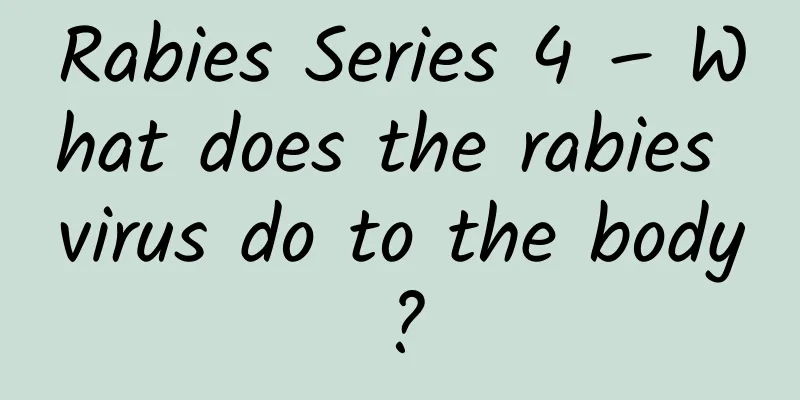
|
From the introduction in the previous issues, we know that rabies is an acute infectious disease shared by humans and animals caused by the rabies virus. It can be transmitted through the saliva of sick animals. Once rabies occurs, there is currently no effective treatment and the mortality rate is almost 100%. (Image source, wikipedia, NIAID) This is a picture of the stained rabies virus attacking cells. The red one looks a bit like a bullet shape, which is the rabies virus. Its genome structure is very simple, but it can solve complex problems by producing five proteins, including infecting mammals, evading the immune system, entering the host brain, replicating itself and infecting more hosts. Let’s take a look at what happens if the rabies virus invades the human body? It all started with a bite from a mad dog. Image source: pixabay The saliva of a rabid dog may carry millions of rabies viruses. The viruses enter the human muscle tissue through wounds and begin to take root there, infecting nearby muscle cells. But in muscle cells, they can replicate without being noticed by the immune system. When enough viruses are produced, they begin to bind to acetylcholine receptors at the junction of muscles and nerves and slip into unsuspecting nerve cells. After entering the nerve cells, the virus needs to solve a big problem, that is, although it enters the nerve cells through the acetylcholine receptor, if we look at the structure of nerve cells, the rabies virus needs to run from the distant cell ends into the core of the cell in order to control the cell to produce more viruses. This involves the basic activity in neurons - axoplasm transport, which can also be simply understood as a conveyor belt. Neurons can use this conveyor belt to transport substances in the cell to the extremities in the forward direction, and can also transport substances absorbed by the extremities (such as neurotrophic factors) to the cell body in the reverse direction. The rabies virus disguises itself as a nutritional factor, is absorbed by the nerve endings, and then moves all the way up to the core of the cell. This stage may take several weeks, which is the incubation period of the virus. The length of the incubation period and the specific bite site are related to the viral load entering the body. Once the virus enters the cell body, it will quickly spread to the central nervous system, replicate in large numbers in motor neurons and eventually reach the brain, at which point the human nervous system will be fatally damaged. The virus then begins to spread "centrifugally", that is, it is transported forward through the axoplasm conveyor belt to your salivary glands, eyes, and sensory nerves under the skin. At this time, the saliva of the infected person is already full of rabies virus, ready to move, waiting to infect the next host. The initial symptoms of rabies may be similar to those of the flu. People may feel weak or unwell, have a fever or headache, and may feel tingling or itching at the site of the bite. As the disease progresses, the infected person may develop hydrophobia, anemophobia, anxiety, mental confusion, mania, aggressiveness, paralysis, etc. within a few days, and eventually die from cardiopulmonary failure. Once rabies breaks out, almost no one can escape it, so it is one of the most deadly viruses known to mankind. Although there are very few cases of cure, there is no truly effective treatment. Currently, the only effective prevention method is to get a rabies vaccine. After vaccination, the human body will produce virus neutralizing antibodies, which can bind to and inactivate the rabies virus. Therefore, if you are bitten by an animal in daily life, you should go to the hospital in time for treatment and get a rabies vaccine. This is a matter of life and death, so you must not be careless! This is the end of the rabies series. I will see you in the next science trivia series. The article is produced by Science Popularization China-Starry Sky Project (Creation and Cultivation). Please indicate the source when reprinting. Author: Science scraps popular science team Reviewer: Wang Chuanlin, Director of Emergency Department, Peking University People's Hospital |
<<: Periarthritis of the shoulder - stop the inflammation of the shoulder
>>: How much do you know about food safety? It is essential for a healthy life
Recommend
What are the nutritional values of red grapes? How to choose high-quality red grapes
Red grapes refer to red grapes, also known as red...
What is the reason why women's period is late?
Menstruation is a very important physical reactio...
Menstrual flow is light and only occurs when you go to the toilet
Under normal circumstances, women have their peri...
What to do if pregnant woman has left side abdominal pain
Abdominal pain in pregnant women is a common phen...
What should pregnant women eat when they have internal heat?
Pregnant women have many physiological problems d...
What are the symptoms of urinary stones in women
Urinary stones are a very terrible disease, and t...
Bright red menstrual blood picture
Irregular menstruation is a condition that many w...
What is the yellow-green watery discharge?
I believe everyone knows that yellow-green watery...
What should I eat to treat low blood sugar during pregnancy?
There are many things that women need to avoid du...
What to do if pregnancy is uncomfortable
During pregnancy, due to certain changes in hormo...
I have had incisional pregnancy for 3 times.
When the fertilized egg implants below the uterus...
Can I drink milk tea during menstruation?
As one of the healthy drinks that women usually l...
Why do I feel tired when my period is coming?
In real life, women are prone to drowsiness and e...
What is the cause of brown discharge in the third month of pregnancy?
Some women often find that their bodies secrete b...
How to make an appointment for the Nine Price
The hpv nine-valent vaccine is a vaccine to preve...









