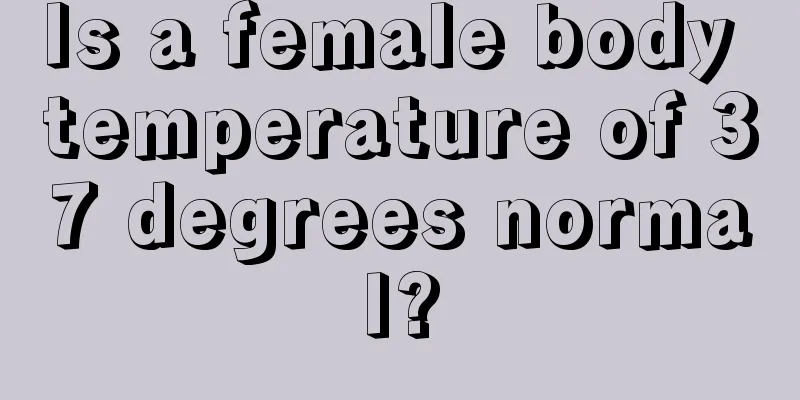A "little guide" for first aid and hemostasis of trauma

|
This is the 4306th article of Da Yi Xiao Hu In the emergency room, we often see patients with various injuries. Because they do not know how to correctly provide first aid to stop bleeding, their various methods of stopping bleeding not only fail to stop bleeding, but sometimes even lead to limb necrosis. Therefore, today I will share with you some basic knowledge about how to provide first aid to stop bleeding after an injury. In daily life or work, once traumatic bleeding occurs, the most common first aid method to stop bleeding is compression hemostasis, which is to press hard on the bleeding site to stop bleeding. We can use handkerchiefs, towels or gauze around us to press hard on the wound, which is simple, fast and has a good hemostasis effect. If you encounter a wound with a large amount of bleeding or a fast blood flow, you should use arterial compression to stop bleeding. When pressing, it is best to find the pulsation site of the artery and press hard on the nearby bone to block or slow down the blood flow, which can stop bleeding quickly and effectively. The following are some of the sites that we commonly use in clinical practice for compression hemostasis, namely the facial artery, superficial temporal artery, common carotid artery, subclavian artery, brachial artery, radial artery, femoral artery, popliteal artery and dorsalis pedis artery, as shown in the figure below. Compression of the superficial temporal artery to stop bleeding is used for traumatic bleeding on the top of the head; compression of the facial artery to stop bleeding is used for traumatic bleeding on the face; compression of the common carotid artery to stop bleeding is used for more serious traumatic bleeding on the head and face, but it is contraindicated to press on both sides at the same time; compression of the subclavian artery to stop bleeding is used for traumatic bleeding on the shoulder and upper limbs; compression of the brachial artery and radial artery to stop bleeding is used for traumatic bleeding on the upper limbs; compression of the femoral artery, popliteal artery and dorsalis pedis artery to stop bleeding is used for traumatic bleeding on the lower limbs. Here we would also like to introduce a very practical method of digital artery compression hemostasis, which is to press the digital arteries on both sides of the base of the finger with the thumb and index finger. This pressing technique can quickly and effectively stop bleeding from finger injuries and is very practical. Of course, compression hemostasis also has its shortcomings, its disadvantages: 1. The hemostatic effect is relatively limited; 2. It is difficult for non-medical professionals to accurately find the location of the arterial pulsation during first aid; 3. It can only be used to stop bleeding temporarily, and the time is controlled within about 15 minutes; 4. The affected limb needs to be elevated to enhance the hemostatic effect. Another simple and effective method is the tourniquet method, which can be used for large wounds on the limbs, heavy bleeding, when compression hemostasis is inconvenient for transportation or has poor results. The medical tourniquet uses a highly elastic rubber strip. In first aid, local materials can be used instead, such as a triangular bandage, cloth strip or towel. When using this method to stop bleeding, you should pay attention to the following points: The tourniquet should be placed at the correct location, the upper limbs should be placed at the upper 1/3 of the upper arm, and the lower limbs should be placed at the upper middle part of the thigh. The tourniquet should be padded to protect the nerves and other tissues in that area and prevent irreversible damage; Be sure to record the time of applying the tourniquet and put the time in a conspicuous place on the tourniquet; Do not use the tourniquet indefinitely. Generally, it should be released after 50 minutes or more, and at most 1 hour. Try not to apply the tourniquet repeatedly. Whether to apply the tourniquet again should be carefully judged according to the situation. If the tourniquet needs to be used again, it is recommended to wait for 10 minutes; Before loosening the tourniquet, be sure to do the preparation work. After loosening it, immediately use direct compression or pressure bandage to stop bleeding to reduce bleeding and avoid heavy bleeding. Cloth bands are limited to temporary use in emergency situations where there is no tourniquet mentioned above. Because cloth bands are not elastic, it is difficult to truly stop bleeding. If they are too tight, they will cause limb damage or ischemic necrosis, so long-term use should be avoided. It is taboo to use iron wire, rope, electric wire, etc. as tourniquets, which can easily cause irreversible damage to muscle nerves and other tissues, leading to sequelae such as limb necrosis. Pressure bandage to stop bleeding is one of the most important and commonly used methods of first aid. It can be widely used in various parts of the body, unlike tourniquets which are limited to the limbs. Cover the wound with clean gauze pads and other dressings, and use bandages, triangular bandages or tape to apply a certain amount of pressure to fix it to achieve the effect of stopping bleeding. If the wound has a large defect, be sure to fill the wound with more dressings before applying pressure bandages. There are two points to note here. The first is that the pressure should be moderate and should not be excessive, which may cause ischemia and damage to nerves and other tissues; the second is that if inelastic materials such as tape are used to fix it, avoid wrapping the limbs in a closed loop to avoid compression of nerves, muscles and other tissues. During first aid, you can also use local materials, such as clean triangular bandages, handkerchiefs, pieces of cloth or towels, to cover the wound with a cloth strip or triangular bandage for temporary pressure bandage. However, since it has no elasticity, excessive pressure should not be applied. It is also necessary to pay attention to the contamination of the wound tissue by the fiber fabric to avoid increasing the difficulty of debridement. The above is a small guide to hemostasis that we often use for first aid when injuries occur in our daily life or work. I hope everyone can save it for emergency use. Author: Shanghai Tongji Hospital Chen Xuemei, head nurse of the emergency department Auditor: Shanghai Tongji Hospital Emergency Surgery |
<<: Why does nipple secretion occur?
>>: Why does it become more and more painful for some people when they do the "Xiaoyanfei" exercise?
Recommend
Symptoms of miscarriage in pregnancy, five symptoms to be aware of
Pregnancy is a happy thing for the whole family, ...
Pregnant women should keep these precautions in mind when measuring blood sugar
Pregnant women should pay attention to controllin...
What to do if your menstrual blood is dark during your period
Under normal circumstances, the color of menstrua...
What are the methods for monitoring ovulation?
Nowadays, physical health is becoming more and mo...
Pregnant for 3 and a half months without abdominal pain or bleeding
If there is no abdominal pain or spotting during ...
Can postpartum sagging and softening of breasts be repaired?
After a woman gives birth, her breasts will be af...
What causes areola spots?
Women will develop various spots during pregnancy...
Can weak positive result be treated with medicine?
Women will suffer significant effects on their bo...
What should I do if I have sex right after IUD insertion?
Women should not have sex when they have just had...
All medicines are toxic. Which medicines are most harmful to the kidneys? And how can we avoid them?
Author: Chen Zhou, attending physician at Shangha...
What is the reason for less blood in menstrual period?
For some women, if the menstrual volume is small ...
What are the other names of yellow-heart kiwifruit (Jinyan, golden fruit, Jinyang kiwifruit, etc.)
...
Woman's limbs are weak and her legs are limp
There are many reasons why women's hands and ...
What medicine to use for sunburned skin
When the weather is hot, even if we take various ...
Dialysis patients, look here! Experts from Changsha Fourth Hospital tell you how to eat scientifically
Dialysis treatment often increases the loss of pr...